R&D
Natural Food Preservatives Materials-Terpenes
R&D

Bacterial contamination and lipid oxidation are the main reasons for the degradations of food quality and the shortening of shelf life. Synthetic preservatives have been used in the food industry for a long time to reduce bacterial contamination, inhibit lipid oxidation, extend shelf life and improve food quality. As the improvement of people living standard, the concerning about the safety of synthetic preservatives have promoted the development of natural food preservatives.

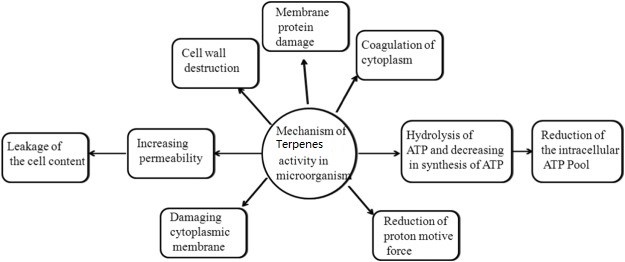
Terpenes extracted from natural plants and comprising the largest class of natural products with more than 30000 compounds (1) are widely used as flavoring, sweeteners, preservatives, and supplements in commercial food processing industries. The wider functions of terpenes in plant biology include light-harvesting pigments in photosynthesis, the attraction of insect pollinators, defense against feedants and pathogens, and as mediators in the interactions of plants with other organisms. (2)
Terpenes and their Antibacterial Activity:
| Cas No. | Terpenes | Antibacterial Activity |
| 5989-27-8 | Limonene | Staphylococcus aureus;
Yersinia enterocolitis |
| 99-87-6 | Para-cymene | Escherichia coli |
| 470-82-6 | 1,8-cineole | Staphylococcus aureus;
Escherichia coli; Salmonella |
| 123-35-3 | Myrcene | Salmonella pullorum |
| 99-85-4 | Gamma Terpinene | Staphylococcus aureus |
| 99-86-5 | Alpha Terpinene | Staphylococcus aureus |
| 80-56-8 | Alpha Pinene | Bacillus cereus |
| 127-91-3 | Beta Pinene | Bacillus cereus |
References
[1] Dagenhardt, J., Kollner, T.G. and Gershenzon, J. (2009) Monoterpene and Sesquiterpene Synthases and the Origin of Terpene Skeletal Diversity in Plants. Phytochemistry, 70, 1621-1637.
[2] Obiloma, A. , Madu, W. , Osuji, G. , Ampim, P. , Weerasooriya, A. and Carson, L. (2019) Terpene-Rich Medicinal Plant Spices for Flavoring of Processed Tropical Food. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 10, 572-577.