R&D, Flavor & Fragrance Industry
What are the Properties and Uses of Borneol
R&D, Flavor & Fragrance Industry

According to《Chinese Pharmacopoeia》, Borneol belongs to a monoterpenoid substance which is from three different sources, including Dextro Borneol, DL-Borneol and Laevo Borneol.
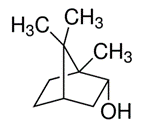
Dextro Borneol is sourcred from the fresh branch and leaf of Cinnamomum cam phora(L.) Presl.
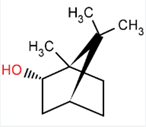
DL-Borneol is produced from alpha pinene through chemical method. It is a mixture mainly composed of borneol and isoborneol
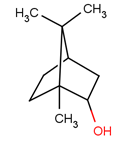
Laevo-Borneol is the crystallization of fresh branch and leaf of Typus physiologies Cinnanloni (Blumea Balsamifera (L.) DC) through distillation of water vapor.
| Borneol | ||||
| Name | Dextro Borneol | DL-Borneol | Laevo Borneol | |
| CAS No | 507-70-0 | 507-70-0 | 464-45-9 | |
| Source | Cinnamomum Camphora (L.) Presl | Pinus | Blumea Balsamifera (L.) DC | |
| Formula |  |
 |
 |
|
| Appearance | White crystalline powder or flake crystal | White needle-like crystals or flake crystal. | white crystalline powder or flake crystal | |
| Odor | Cool camphor smell | Cool camphor smell | Cool camphor smell | |
| Melting Point | 204 – 209°C | 205 – 210°C | 201 – 205°C | |
| Optical Rotation | +34° ~ +38° | / | -36.5° ~ -38.5° | |
| Isoborneol | Not be detected | 45.0% max | 0.50% max | |
| Camphor | 3.0% max | 0.50% max | 10.0% max | |
| PH | / | Approval | / | |
| Non-volatile matter | / | 0.035% max | / | |
| Moisture | / | Approval | / | |
| Heavy Mental | / | 0.0005%max | / | |
| As salt (ppm) | / | 0.0002%max | / | |
| Borneol Content | D-borneol ≥96.0% | DL-borneol ≥55.0% | L-borneol ≥85.0% | |
Borneol is widely used in preparation of rosemary, lavender and other fragrances which is applied in the production of household products like soap and detergent.
Borneol is also used in pharmaceutical field. Borneol offers many health benefits, including improved digestion (via the stimulation of gastric juices) and better blood circulation. It also effectively treats bronchial symptoms to improve lung function and ease breathing (helpful for sufferers of bronchitis and asthma). Like many of its sibling terpenes, it has been found to reduce anxiety.
Borneol also assists in the healing of wounds. Historically, it has been incorporated into topical treatments for such applications, including the treatment of hemorrhoids. Combined with other terpenes that convey sedative qualities — such as myrcene and linalool — the terpene can effectively combat insomnia. It is also antibacterial and antiseptic.
Borneol exemplifies the dynamics of the entourage effect, a theory that cannabinoids and terpenes work together, synergistically, to offer particular therapeutic and medicinal benefits to humans via supplementation of the mammalian endocannabinoid system (ECS). Borneol amplifies the permeability of the blood/brain barrier, allowing other molecules and compounds to more efficiently bind with specialized receptors in the brain and central nervous system.
Meanwhile, multiple studies have demonstrated the wide-ranging medicinal efficacy of borneol including its pronounced role as an anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, and cancer killer.
A 2017 study entitled “Terpenes from Forests and Human Health” and published in the journal Toxicological Research investigated how borneol reduced inflammation of the lungs. Concluded the researchers, “Borneol alleviated acute lung inflammation by reducing inflammatory infiltration, histopathological changes, and cytokine production.”
A 2013 study published in the journal PLOS ONE and entitled “Natural Borneol, a Monoterpenoid Compound, Potentiates Selenocystine-induced Apoptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells” revealed the anti-cancer properties of this terpene.
The study’s researchers concluded, “Borneol effectively synergized with SeC to reduce cancer cell growth through the triggering apoptotic cell death. These results reveal that borneol strongly potentiates SeC-induced apoptosis in cancer cells by enhancement of cellular uptake. Borneol could be further developed as a chemosensitizer of SeC in treatment of human cancers.”